PPT Triangle Inequality (Triangle Inequality Theorem) PowerPoint Presentation ID3028420
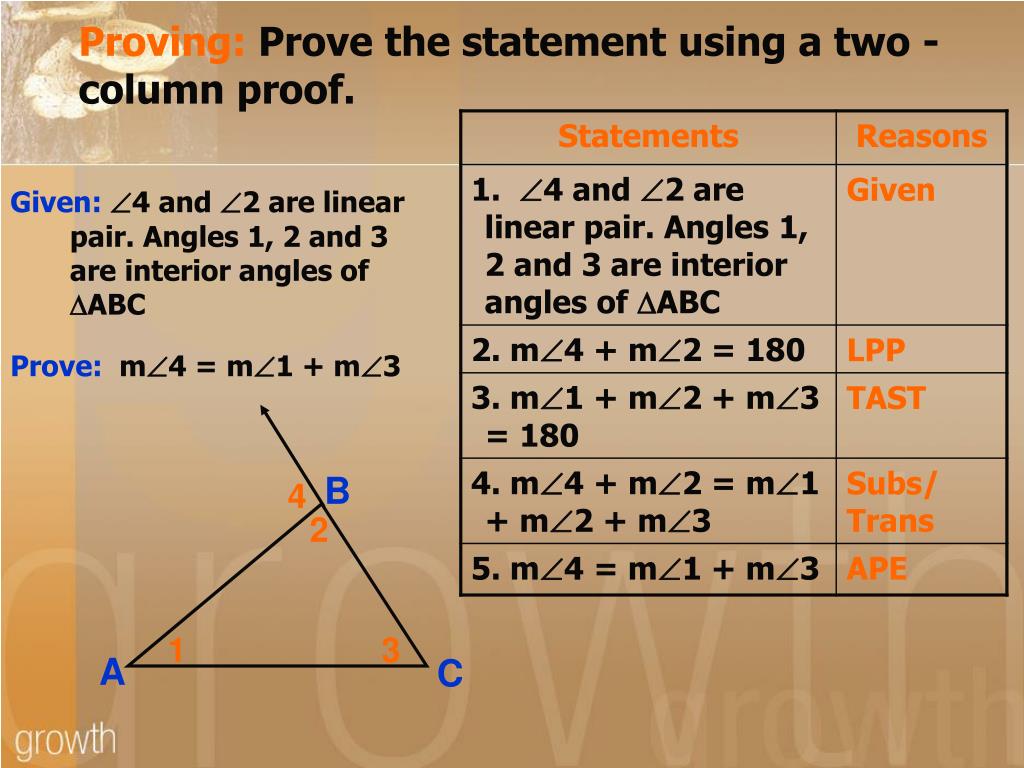
The triangle inequality theorem states that, in a triangle, the sum of lengths of any two sides is greater than the length of the third side. Suppose a, b and c are the lengths of the sides of a triangle, then, the sum of lengths of a and b is greater than the length c. Similarly, b + c > a, and a+ c > b.

CALCULUS. Proof Triangle Inequality (5) YouTube
The triangle inequality states that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the length of the remaining side. It follows from the fact that a straight line is the shortest path between two points. The inequality is strict if the triangle is non- degenerate (meaning it has a non-zero area). Contents Examples Vectors

Triangle Inequality Simple Proof YouTube
The triangle inequality is a defining property of norms and measures of distance. This property must be established as a theorem for any function proposed for such purposes for each particular space: for example, spaces such as the real numbers, Euclidean spaces, the L p spaces ( p ≥ 1 ), and inner product spaces . Euclidean geometry

Inequality Proof using the Reverse Triangle Inequality YouTube
The Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality holds for any inner Product, so the triangle inequality holds irrespective of how you define the norm of the vector to be, i.e., the way you define scalar product in that vector space.

Triangle Inequality Theorem Definition & Examples Cuemath
Triangle Inequality. Let and be vectors. Then the triangle inequality is given by. (1) Equivalently, for complex numbers and , (2) Geometrically, the right-hand part of the triangle inequality states that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the length of the remaining side. A generalization is.

Triangle Inequality TheoremDefinition & Examples Cuemath
Triangle inequality theorem. The Triangle Inequality Theorem states that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the length of the third side. Consider our 3−4−5 triangle example above. Add up any two sides of it. The sum of any of those two sides must be greater than the remaining side: 3+4>5 3 + 4 > 5.

19+ triangle inequality theorem calculator Ikafnurhayati
The proof is below. Proof Geometrically, the triangular inequality is an inequality expressing that the sum of the lengths of two sides of a triangle is longer than the length of the other side as shown in the figure below. The proof is as follows. Let a a and b b be real vectors.
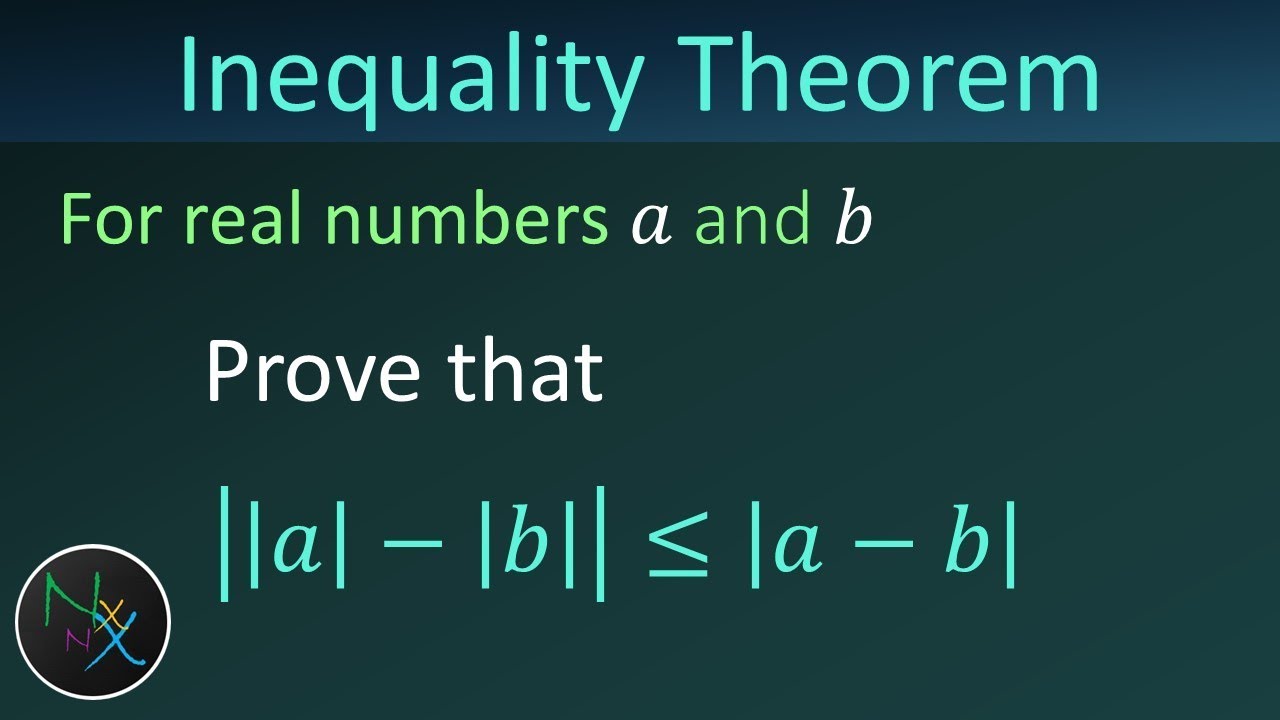
Reverse Triangle Inequality Absolute Value Proof YouTube
The proof of the triangle inequality follows the same form as in that case. 8. Sas in 7. d(f;g) = max a x b jf(x) g(x)j: This is the continuous equivalent of the sup metric. The proof of the triangle inequality is virtually identical.

How to Prove the Triangle Inequality for Complex Numbers YouTube
1 That a metric must obey the triangle inequality is indeed one of the axioms of a metric space. - user1236 Jul 28, 2015 at 1:04 1 Consider the possibilities for a and b: each can be negative, zero, or positive. Thus there are at most nine possibilities to check out separately. You can do it! Be brave! - richard1941 Jan 24, 2018 at 1:18 2
Inequality Proof using Both the Triangle Inequality and Reverse Triangle Inequality YouTube
The triangle inequality is a theorem that states that in any triangle, the sum of two of the three sides of the triangle must be greater than the third side. For example, in the following diagram, we have the triangle ABC: The triangle inequality tells us that: The sum AB+BC must be greater than AC. Therefore, we have AB+BC>AC.

Proof Reverse Triangle Inequality Theorem Real Analysis YouTube
Proof of triangle inequality theorem Thus, we can conclude that the sum of two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side. Video Lesson on BPT and Similar Triangles 2,36,417 Also, read: Triangles Isosceles Triangle Theorems Congruence Of Triangles Class 9 Triangles For Class 10 Example Problems Q.1.

Triangular inequality Proof (easy method) YouTube
The triangle inequality is a very simple inequality that turns out to be extremely useful. It relates the absolute value of the sum of numbers to the absolute values of those numbers. So before we state it, we should formalise the absolute value function. 🔗 Definition 5.4.1. Let , x ∈ R, then the absolute value of x is denoted | x | and is given by
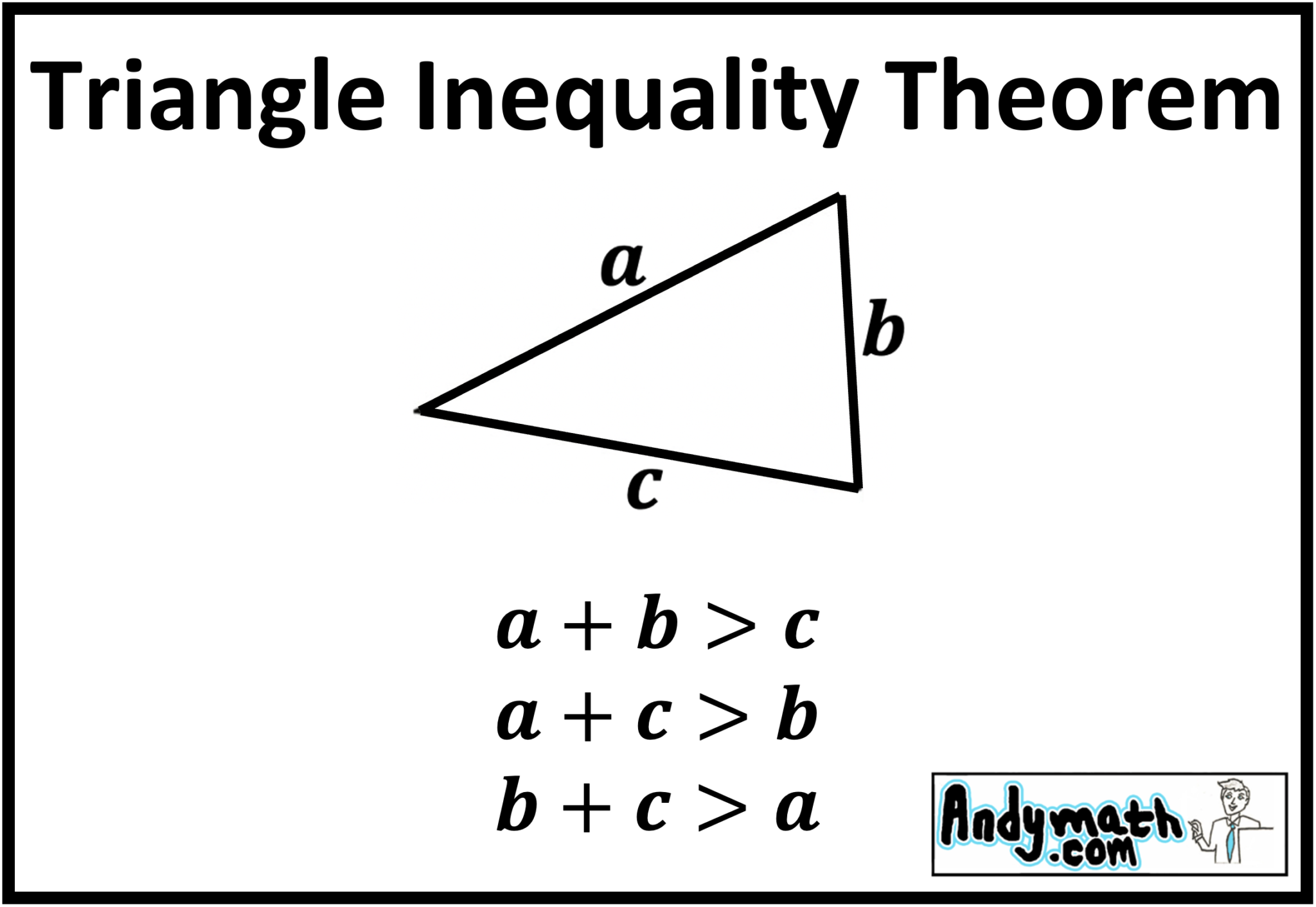
Triangle Inequality Theorem
known that we can prove the triangle inequality in the broad sence, i.e. the ` '-version of (1.1), by algebraic argument. It is not exactly the triangle inequality in the sense of Euclidean geometry, because the point A is on the segment BC in case AB + AC = BC. For details of them, Subsection 1.2 (in particular Remark 1.3) will mention.
Triangle Inequality Theorem Definition, Proof, Examples
Proof: Extend BA to point D such that AD = AC, and join C to D, as shown below: We note that ∠ACD = ∠D, which means that in ∆ BCD, ∠BCD > ∠D. Sides opposite larger angles are larger, and thus: BD > BC AB + AD > BC AB + AC > BC (because AD = AC) This completes our proof. We can additionally conclude that in a triangle:

Triangle Inequality for Real Numbers Proof YouTube
Let us take our initial example. We could make a triangle with line segments having lengths 6, 8, and 10 units. This is because those line segments satisfy the triangle inequality theorem. 6 + 8 = 14 and 10 < 14. 8 + 10 = 18 and 6 < 18. 6 + 10 = 16 and 8 < 16.

Reverse Triangle Inequality Proof YouTube
Use the Triangle Inequality Theorem. Check to make sure that the smaller two numbers add up to be greater than the largest number. 4 + 8 = 12 4 + 8 = 12 and 12 > 11 12 > 11 so yes these lengths make a triangle. Example 4.26.4 4.26. 4. Find the length of the third side of a triangle if the other two sides are 10 and 6.